Multimodal Monday #39: Generative Giants, Retrieval Weaklings
Weeks of December 29 - January 4, 2026: Research reveals why MLLMs like Qwen2-VL fall down, MegaRAG builds multimodal knowledge graphs without manual construction, HiStream generates 1080p video 107x faster, and Google DeepMind discovers geometric memory in sequence models.

Happy New Year! This roundup covers the past two weeks and 2026 has started with a bang, it is going to be a big year for multimodal AI.
Quick Hits (TL;DR)
- MLLMs can't retrieve what they can generate. New research shows models like Qwen2-VL and Paligemma2 fail at zero-shot multimodal retrieval despite excelling at generation. CLIP still wins for search tasks.
- Sequence models discovered a new memory type. Google DeepMind identified geometric memory in deep sequence models, where embeddings encode global entity relationships rather than just co-occurrence patterns.
- Video generation hit a speed breakthrough. HiStream eliminates spatial, temporal, and timestep redundancy to generate 1080p video 107x faster than previous methods.
Tools, Models and Techniques
Tencent HY-Motion 1.0
Tencent released a billion-parameter text-to-motion model using Diffusion Transformer architecture and flow matching. The model generates 3D character animations from text prompts.
Why it matters: You can now generate fluid, diverse character animations without motion capture data.
Links: Project Page | Github | Hugging Face | Technical report
Diffusion Knows Transparency (DKT)
DKT repurposes video diffusion models for transparent object depth and normal estimation. It achieves zero-shot SOTA on ClearPose/DREDS benchmarks, runs at 0.17s per frame, and maintains temporal consistency across videos.
Why it matters: Transparent objects finally get reliable depth estimation without specialized training data.
Links: Hugging Face | Paper | Website | Models
LongVideoAgent
A multi-agent framework where a master LLM coordinates a grounding agent for segment localization and a vision agent for observation extraction. The system uses reinforcement learning to optimize multi-agent cooperation with step limits.
Why it matters: You can now query hour-long videos with targeted questions instead of processing entire timelines.
Links: Paper | Website | GitHub
Qwen-Image-2512
Qwen's new text-to-image model delivers more realistic humans, finer natural textures, and stronger text rendering. It sets a new SOTA benchmark for image generation quality.
Links: Hugging Face | GitHub | Blog | Demo | GGUF
Yume-1.5
A text-controlled interactive world generation model that creates explorable 3D environments. Users can navigate and interact with generated spaces in real time.
Links: Website | Hugging Face | Paper
TwinFlow
Enables one-step generation on large models using self-adversarial flows. The approach eliminates iterative sampling while maintaining output quality.
Links: Hugging Face
Stable Video Infinite 2.0 Pro
The new version launched with immediate ComfyUI wrapper support from Kijai. Models are already available for download and integration.
Links: Hugging Face | GitHub
Soprano
An ultra-lightweight TTS model that generates 10 hours of 32kHz audio in under 20 seconds. It streams with sub-15ms latency using only 80M parameters and less than 1GB VRAM.
Links: GitHub
Wan-NVFP4
A fast video model claiming 28x faster render speeds than previous versions. Released by lightx2v on Hugging Face.
Links: Hugging Face
JavisGPT
A unified multi-modal LLM for sounding-video comprehension and generation. The model handles video analysis and audio-visual synthesis in one framework.
Links: Paper | GitHub | Models
Dream-VL & Dream-VLA
Open vision-language and vision-language-action models using a diffusion language model backbone. Both models integrate visual understanding with either language or robotic action outputs.
Links: Paper | Hugging Face | Hugging Face | GitHub
HyperCLOVA X SEED Omni 8B
A unified multimodal model handling text, vision, audio, and video inputs with text, image, and audio outputs.
Links: Hugging Face
AMD ROCm
AMD published a guide for accelerating multimodal inference in vLLM using batch-level dynamic programming switches.
Links: Blog
Research Highlights
Generative Giants, Retrieval Weaklings: Why do Multimodal Large Language Models Fail at Multimodal Retrieval?
MLLMs like Qwen2-VL and Paligemma2 fail at zero-shot multimodal retrieval despite excelling at generation. Using sparse autoencoders, researchers identified three limitations: training objectives optimize for generation not retrieval, evaluation focuses on generative tasks, and autoregressive architectures compute poor similarity scores.
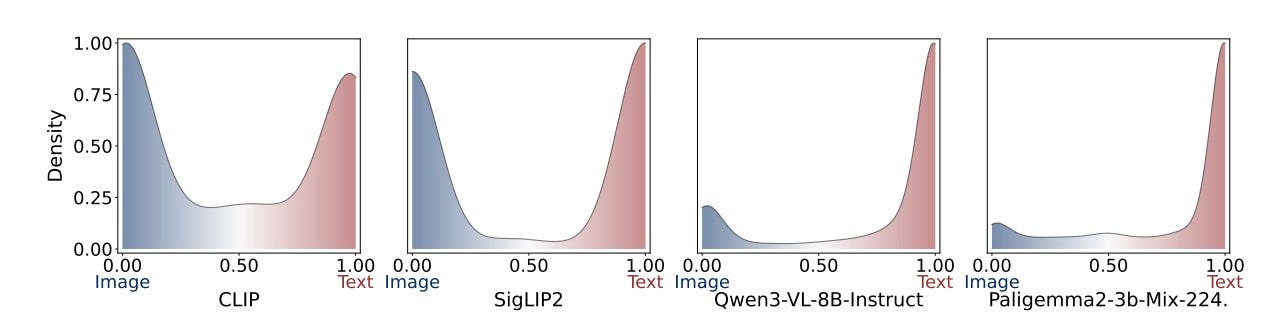
Why it matters: You need specialized models like CLIP for retrieval tasks until MLLMs address these architectural limitations.
Links: Paper
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
ReaSeq solves two problems in recommender systems: knowledge poverty in ID-based representations and systemic blindness to off-platform user interests. The framework uses reasoning to incorporate world knowledge into sequential modeling.
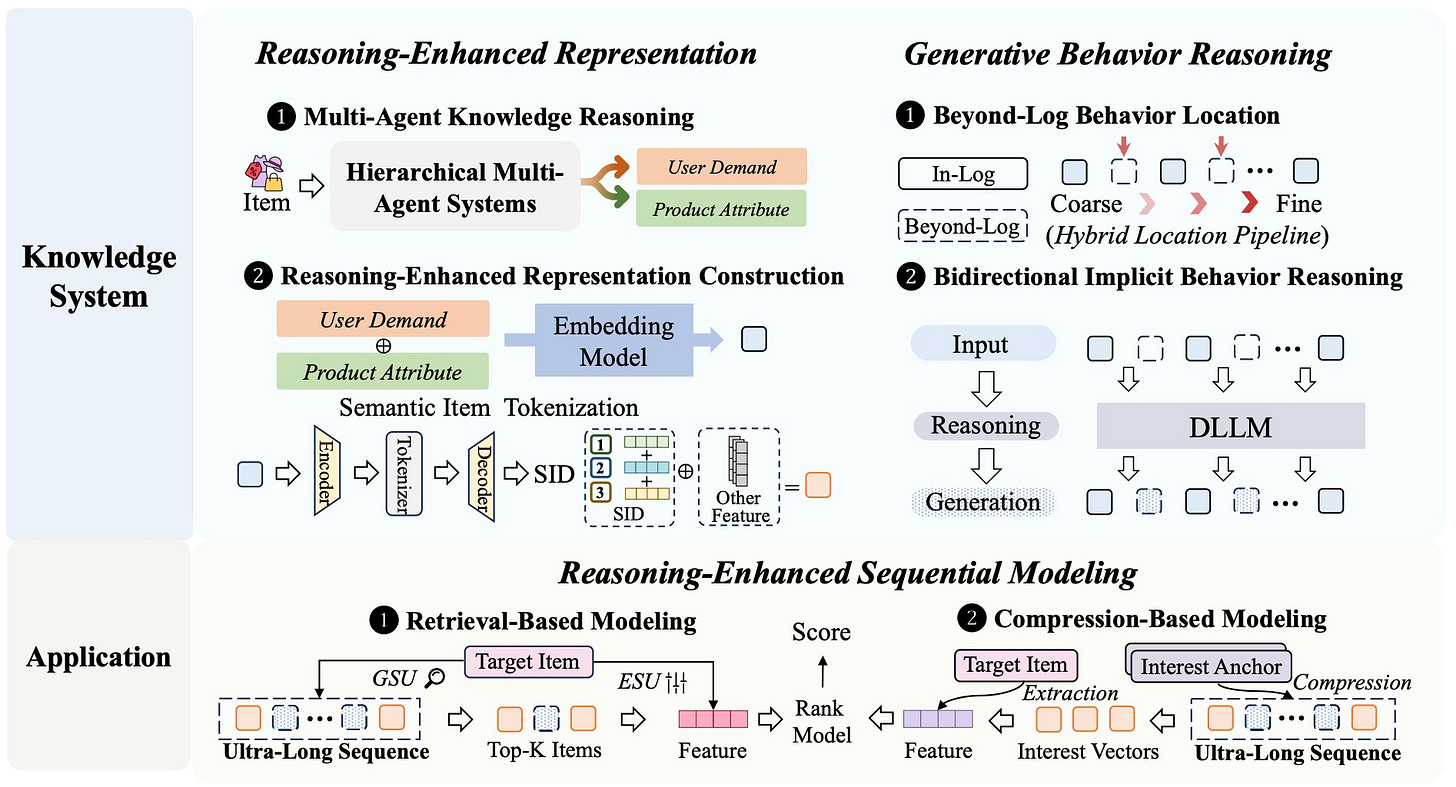
Why it matters: Recommendation systems can now reason about user interests beyond platform interaction logs.
Links: Paper
MegaRAG: Multimodal Knowledge Graph-Based Retrieval Augmented Generation
MegaRAG automatically constructs multimodal knowledge graphs integrating text, visual, and spatial information from documents. It uses a two-round, page-based approach where LLMs extract entities in parallel then refine the graph by retrieving relevant subgraphs.
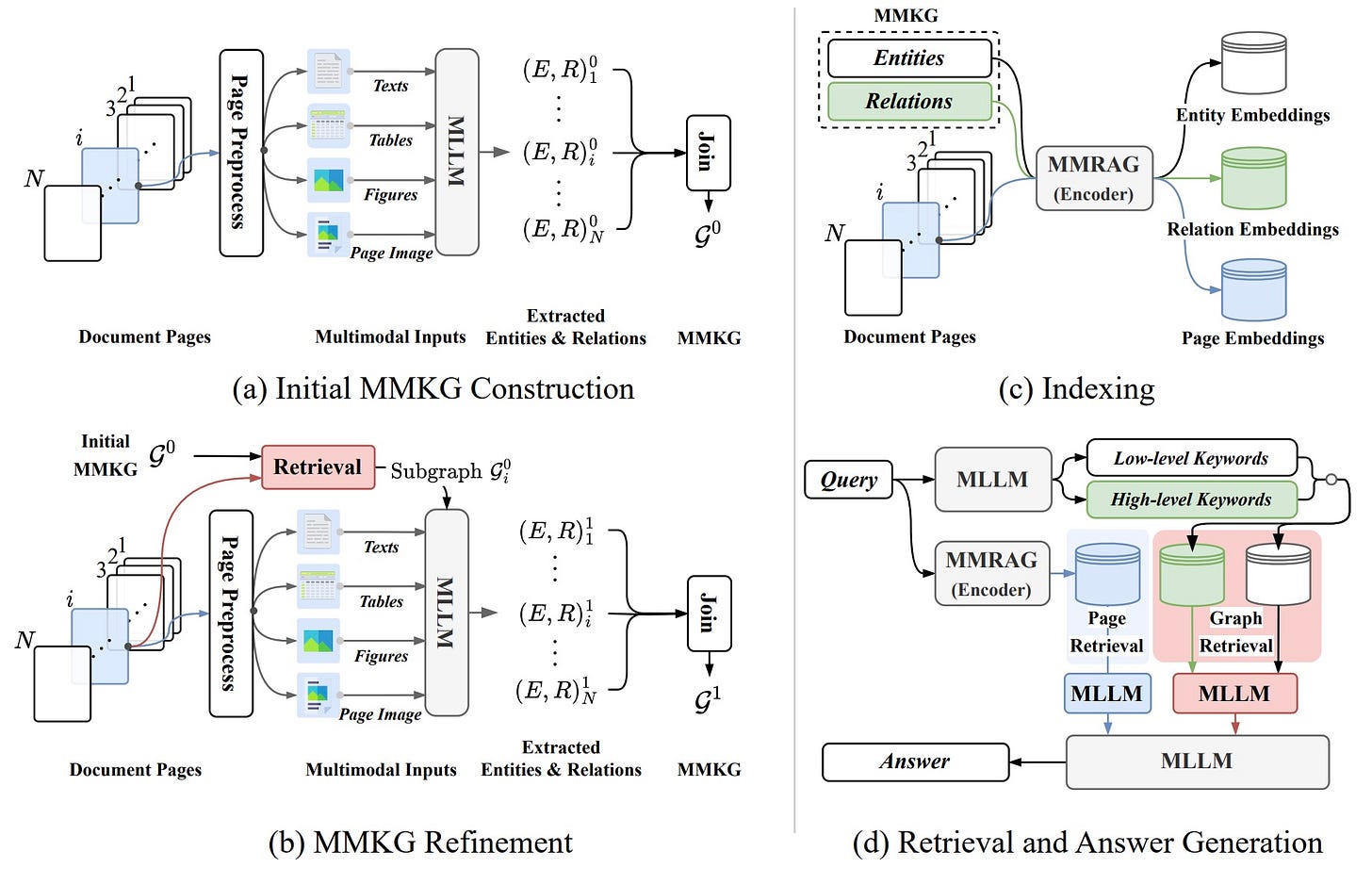
Why it matters: RAG systems can now handle visually rich documents without manual graph construction.
Links: Paper
Retrieval-augmented Prompt Learning for Pre-trained Foundation Models
This framework enhances prompt learning by decoupling knowledge from memorization. The approach addresses instability in low-resource settings where parametric models overfit to shallow patterns.
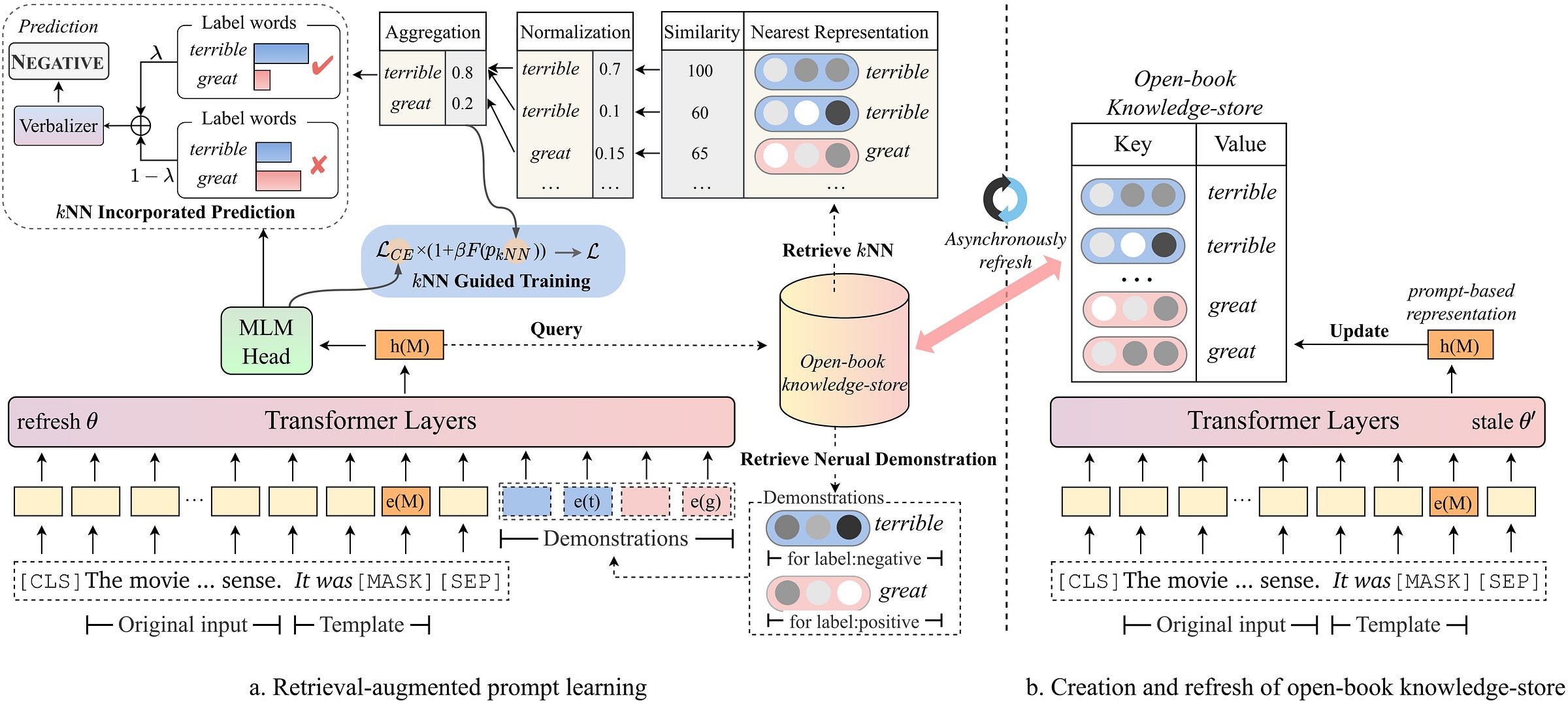
Why it matters: Prompt learning becomes reliable even with limited training data.
Links: Paper | GitHub
Latent Implicit Visual Reasoning
LIVR discovers visual reasoning tokens without explicit supervision. The method outperforms approaches requiring costly annotations.
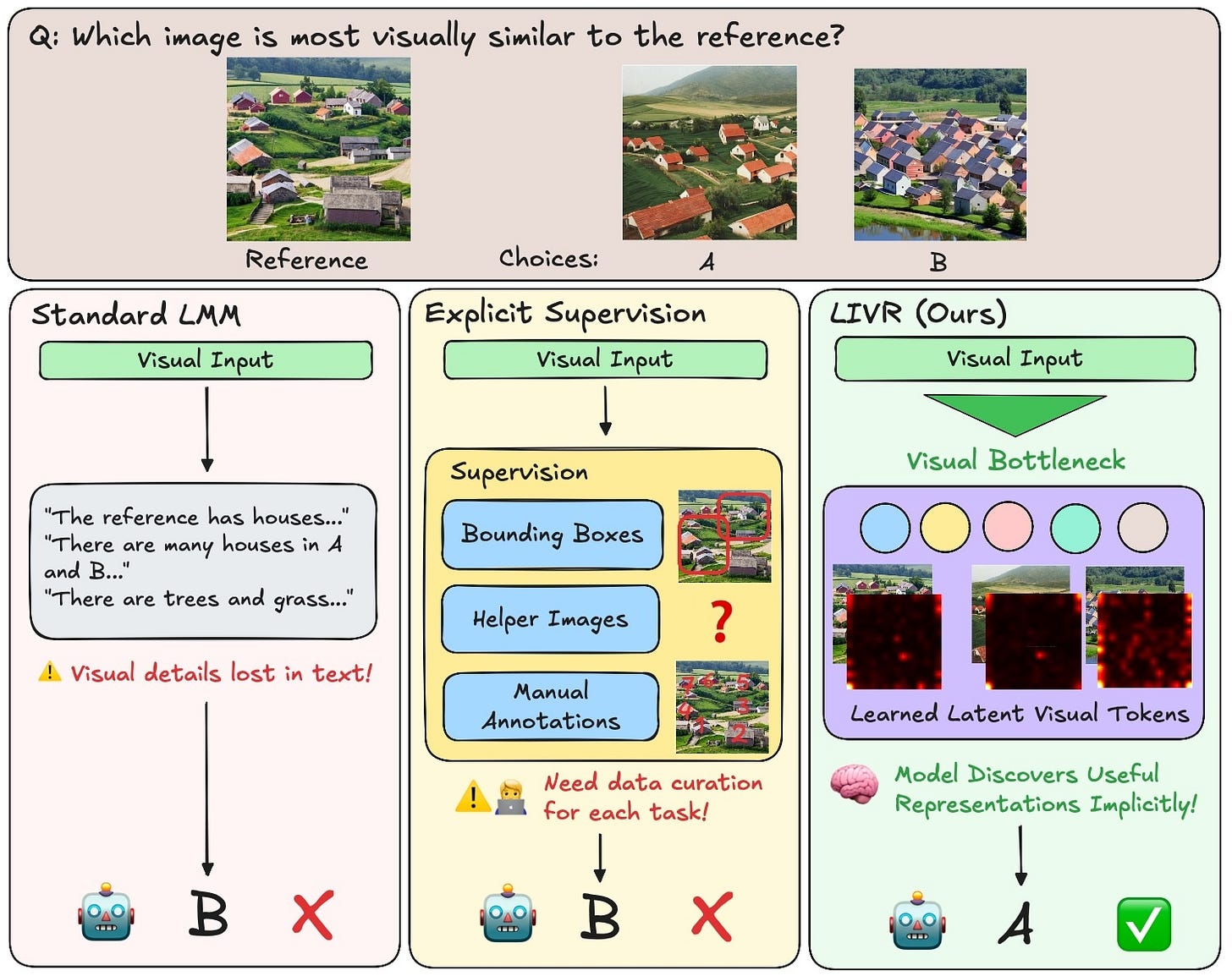
Why it matters: Visual reasoning models no longer need expensive manual labeling.
Links: Paper
Geometric Memory in Sequence Models
Google DeepMind identified geometric memory in deep sequence models, where embeddings encode global relationships between all entities including those never co-occurring in training. This contrasts with associative memory's brute-force lookup approach.
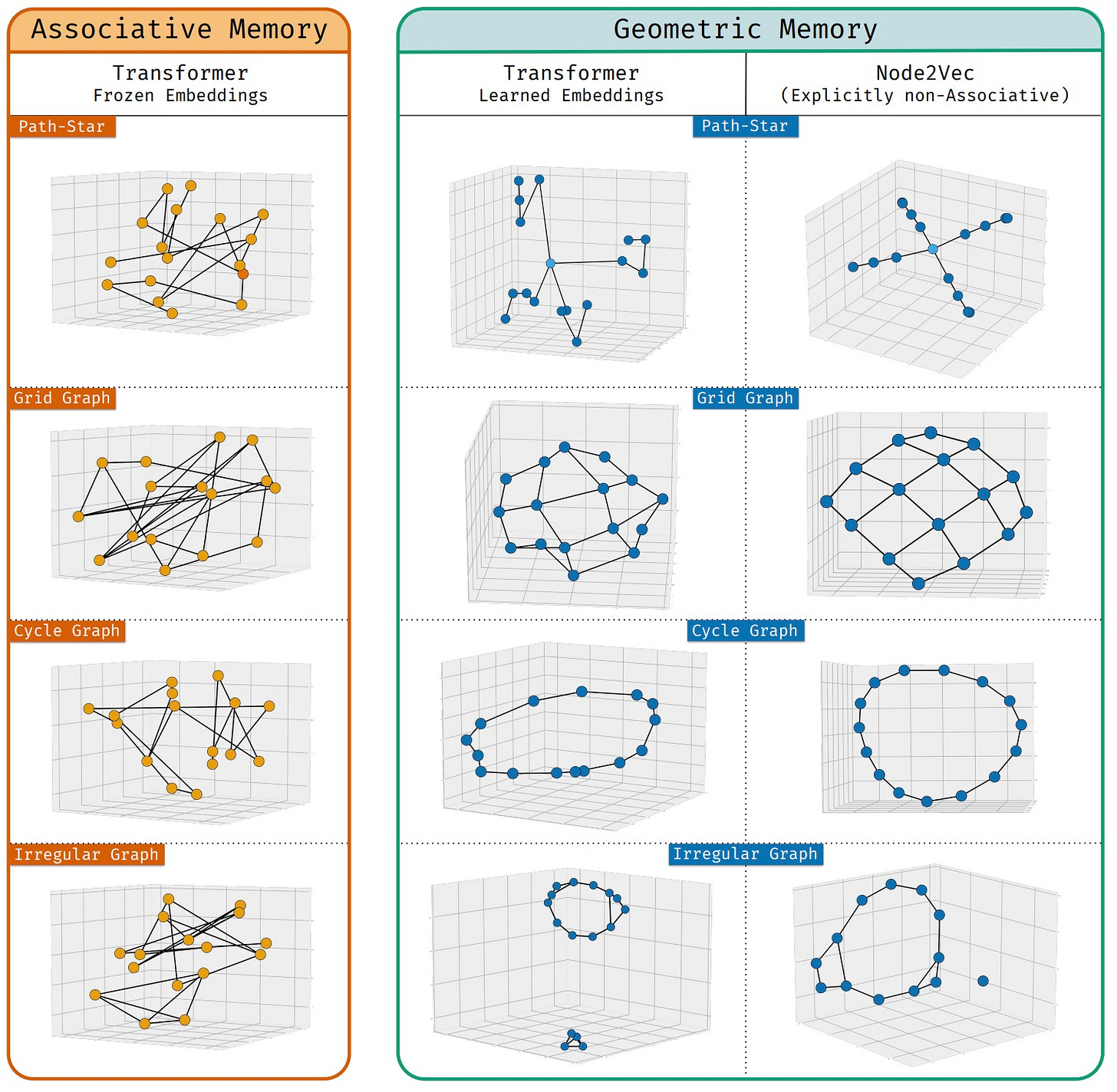
Why it matters: Sequence models can now perform multi-step reasoning through single-step navigation in embedding space.
Links: Paper
Step-DeepResearch
A 32B parameter research agent matching OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch through atomic capability training. It decomposes research into planning, information gathering, verification, and writing, achieving 61.42 on ResearchRubrics.
Links: Paper | GitHub
SpatialTree
A 4-level cognitive hierarchy mapping spatial abilities in MLLMs from perception to agentic competence. Benchmarks 27 sub-abilities across 16 models and reveals transfer patterns.
Links: Website | Paper | Benchmark
FlowBlending
Stage-aware multi-model sampling for fast and high-fidelity video generation. The approach optimizes different models for different stages of the generation process.
Links: Paper
SpaceTimePilot
Adobe's video diffusion model disentangles space and time for controllable rendering. From a single input video, it enables independent control of camera viewpoint and motion for bullet-time, slow motion, and mixed trajectories.
Links: Website | Paper
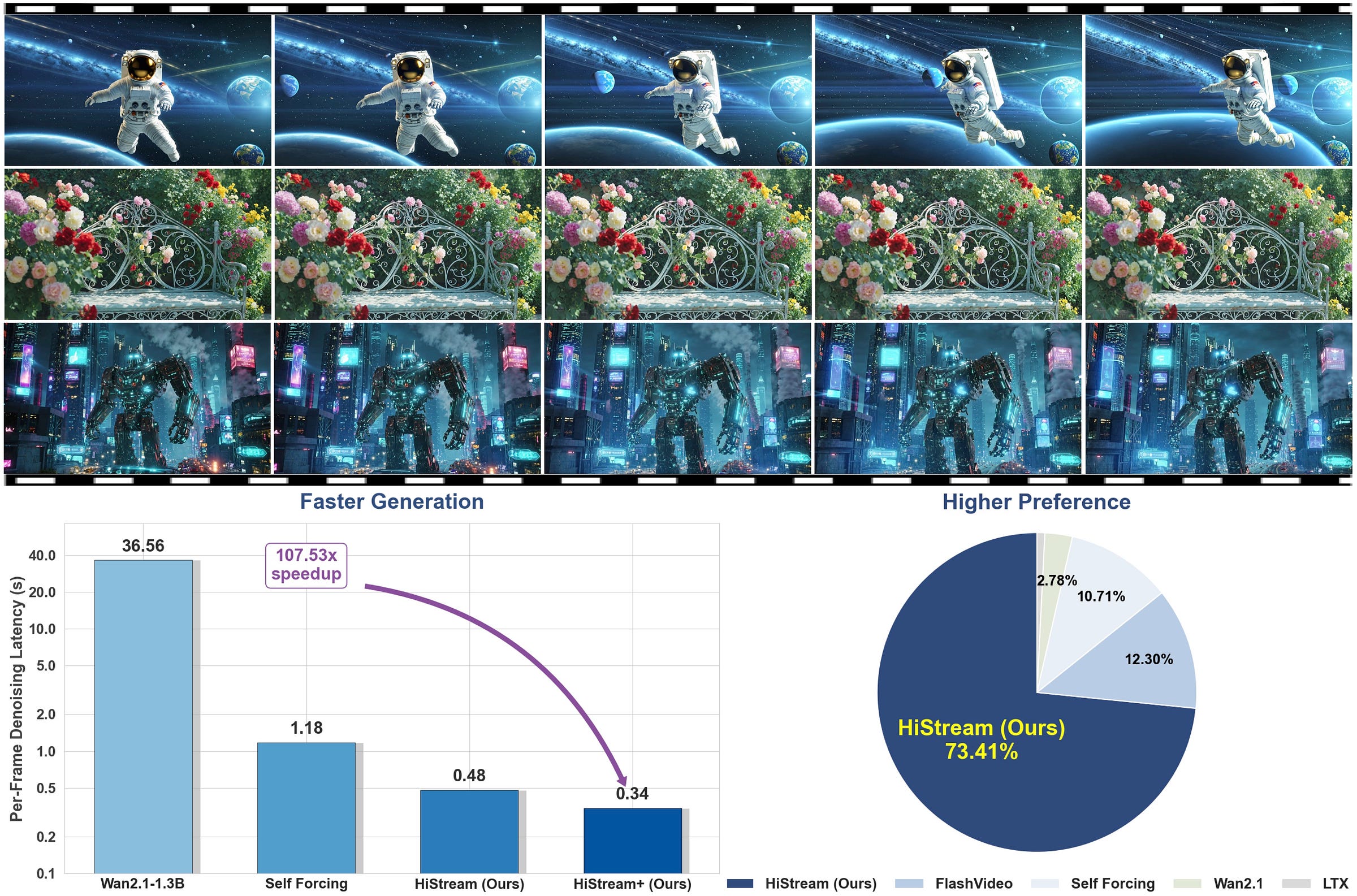
HiStream
Meta's autoregressive framework for 1080p video generation eliminates spatial, temporal, and timestep redundancy. HiStream achieves SOTA quality with up to 107.5x speedup.
Links: Website | Paper | Code
InsertAnywhere
Bridges 4D scene geometry and diffusion models for realistic video object insertion. The method maintains spatial and temporal consistency across frames.
Links: Paper | Website
Robust-R1
A framework making multimodal models robust to visual degradations through explicit degradation-aware reasoning chains. Achieves SOTA robustness on R-Bench while maintaining interpretability.
Links: Paper | Demo | Dataset
StoryMem
ByteDance's multi-shot long video storytelling framework with memory. The system maintains narrative consistency across extended video sequences.
Links: Website | Code
Spatia
Microsoft's video generation system maintains a 3D scene point cloud as persistent spatial memory. Enables long-horizon, spatially consistent video generation with explicit camera control and 3D-aware editing.
Links: Website | Paper | Video
DiffThinker
Enables generative multimodal reasoning with diffusion models. The approach integrates reasoning capabilities directly into the diffusion generation process.
Links: Paper | Website
Trends & Predictions
MLLMs Are Not Taking Over... Yet
New research reveals a fundamental problem with multimodal large language models. Despite their impressive text generation, models like Qwen2-VL and Paligemma2 fail at zero-shot multimodal retrieval. They can describe an image in detail but cannot tell you which image best matches a query. They can answer complex questions about a video but cannot find relevant videos in a database.
The problem is architectural. MLLMs train to generate text, not retrieve images. They optimize for autoregressive generation, not similarity computation. Their evaluation metrics focus on generation quality, not retrieval accuracy.
This matters for your systems. If you need multimodal retrieval, use CLIP. It was designed for retrieval. MLLMs were not. CLIP runs faster, retrieves more accurately, and trains easier. The specialized model wins.
This pattern extends beyond retrieval. Step-DeepResearch shows a 32B parameter model matches much larger research agents by focusing on atomic capabilities. HiStream achieves 107x speedup by eliminating redundancy rather than adding parameters. Soprano runs real-time speech synthesis on consumer hardware with 80M parameters.
The trend is clear. Specialized models beat general-purpose models at specific tasks. You need to match your model to your task. The ecosystem is diversifying, not consolidating. Different problems need different architectures.
MLLMs will improve at retrieval. Someone will solve the architectural issues. But that day is not today. Build with the tools that work now, not the tools you hope will work later.
Community + Shoutouts
ComfyUI Segmentation Agent
Adam Barbato released an LLM-based character segmentation agent for ComfyUI using SAM 3.
Links: GitHub

CosyVoice 3 ComfyUI
Machine Delusion released a voice cloning node pack featuring CosyVoice 3 for ComfyUI.
Links: Announcement | GitHub
SAM3 Video Tracking in X-AnyLabeling
Important_Priority76 integrated SAM3 video object tracking into X-AnyLabeling for easy annotation workflows.
Links: Reddit | GitHub
That's a wrap for Multimodal Monday #39! This week exposed fundamental limitations in current multimodal models while demonstrating paths forward. MLLMs excel at generation but fail at retrieval due to architectural constraints. Meanwhile, HiStream proves speed comes from eliminating redundancy, MegaRAG shows automatic multimodal knowledge graphs work, and geometric memory reveals how models encode relationships they never saw in training.
Ready to build multimodal solutions that actually work? Let's talk
