Multimodal Monday #41: Small Models Win, Vision Models Fail
Week of January 12-18, 2026: ReinPool cuts retrieval storage by up to 1000x, vision models fail basic tests that 6-year-olds ace, ShowUI-Aloha learns to click and scroll from demonstrations, and agents manage their own memory with frameworks like AgeMem and SimpleMem.

Quick Hits (TL;DR)
- AI vision is still learning to see - Despite the hype, state-of-the-art models still struggle with basic visual reasoning tasks that a 6-year-old can solve, highlighting a critical gap between “describing” an image and truly “understanding” it.
- Multimodal retrieval gets smarter and faster - New frameworks like ReinPool and FastLane are solving the storage and speed bottlenecks of advanced retrieval systems, making it feasible to search massive multimodal datasets with high precision.
- Video is becoming a 3D engine - Research like UniSH and VerseCrafter is blurring the line between 2D and 3D, demonstrating that we can now extract high-fidelity 3D geometry and 4D motion directly from standard video footage without complex capture setups.
🛠️ Tools, Models and Techniques
Ministral 3
Mistral AI released a new family of compact language models (3B, 8B, 14B) designed for edge devices. These models aren’t just small; they’re built with integrated image understanding and reasoning capabilities, making them powerful tools for local multimodal applications.
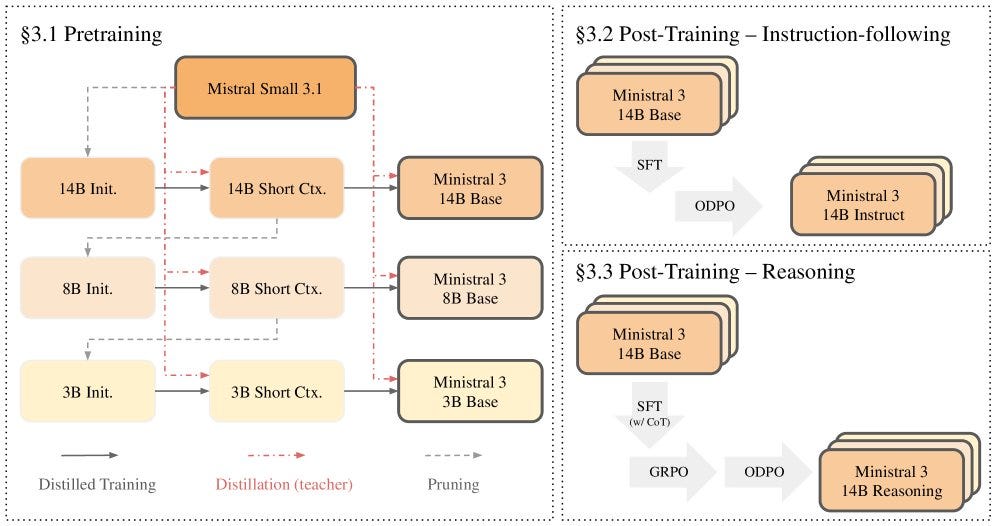
Why it matters: Running capable multimodal models on-device is the holy grail for privacy and latency. Ministral 3 brings us closer to having smart, visual assistants that run entirely on your phone or laptop without needing a cloud connection.
Hugging Face | Paper
FLUX.2 [klein]
Black Forest Labs dropped a highly efficient image generation model that runs on consumer GPUs (13GB VRAM). It handles text-to-image, editing, and multi-reference generation in a single model, generating high-quality results in under a second.

Why it matters: Speed and accessibility are key for creative workflows. A model that can generate and edit images this fast on consumer hardware opens up real-time creative applications that were previously impossible.
Blog | Demo
STEP3-VL-10B
StepFun released a lightweight 10B parameter multimodal model that punches above its weight class. It excels in visual perception and complex reasoning, challenging the notion that you need massive models for high-level multimodal intelligence.
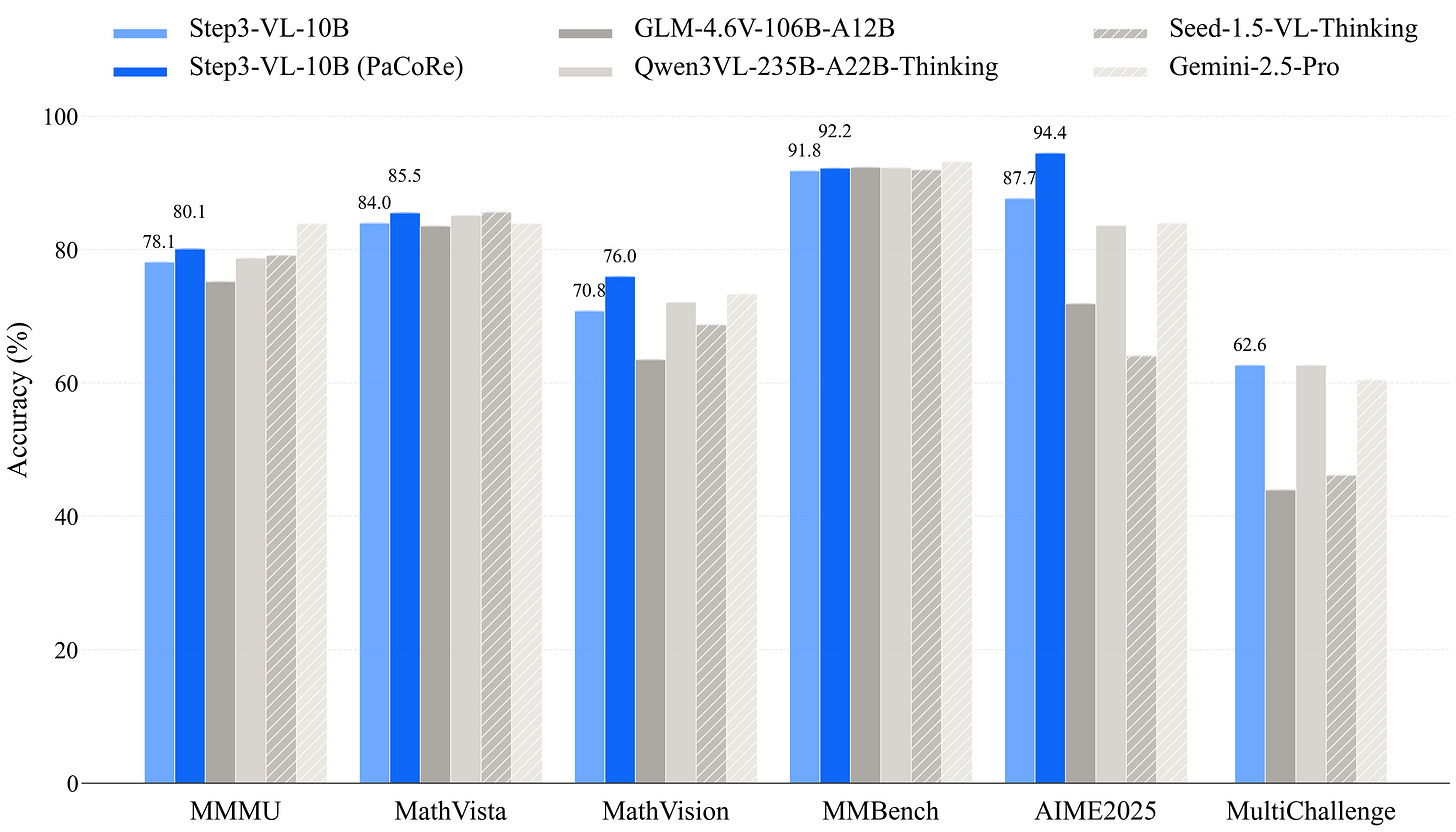
Why it matters: Efficiency is the new frontier. Models like STEP3-VL show that we can get frontier-level performance with a fraction of the compute, making advanced multimodal AI more accessible and cost-effective to deploy.
Hugging Face | Paper
UniSH
This new framework reconstructs 3D scenes and human poses from a single video stream. It estimates scene geometry, camera parameters, and human shape simultaneously, creating a cohesive 3D representation from flat video.
Why it matters: Creating 3D content usually requires complex setups. UniSH turns any video into a source of 3D data, which has huge implications for VR/AR content creation, game development, and digital twin applications.
Project Page | Paper
ShowUI-Aloha
A flow-based generative model that learns to use GUIs from human demonstrations. It can generate smooth mouse movements and clicks, adapting to new task variants after being taught a workflow just once.
Why it matters: This is a step towards true “computer-using” agents. Instead of relying on brittle scripts, agents that can learn to interact with software visually like a human can automate complex, dynamic workflows across any application.
Project Page | GitHub
More Models, Tools and Other Releases:
- TranslateGemma: Google’s new family of open translation models (4B, 12B, 27B) supporting 55 languages. Announcement
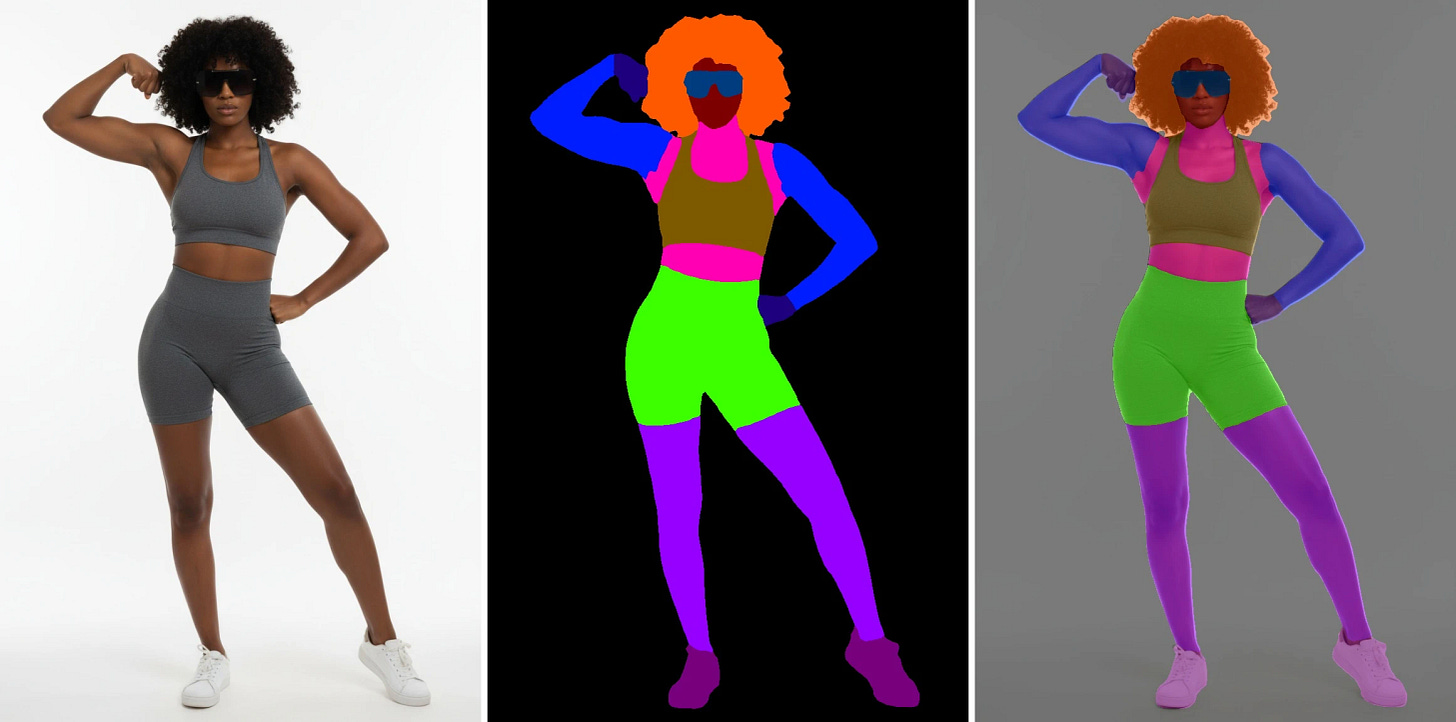
- FASHN Human Parser: A fine-tuned SegFormer model specifically for parsing humans in fashion images. Hugging Face

- VIBE: An editor that lets you modify images using natural language instructions. Paper
- Claude Cowork: A new teamwork layer for Claude allowing multi-user collaboration and shared knowledge bases. Blog
- VerseCrafter: Enables precise 4D geometric control for video generation using point clouds. Project Page
- Action100M: Meta’s massive new dataset for video action recognition. Paper
- DeepSeek Engram: A lookup-based memory module for faster knowledge retrieval in LLMs. GitHub
🧠 Research Highlights
BabyVision: AI Vision is Still in Its Infancy
A sobering new benchmark reveals that state-of-the-art Multimodal LLMs score only 49.7% on basic visual reasoning tasks, compared to 94.1% for human adults. Even the best models perform below the level of a 6-year-old on tasks that require genuine visual understanding rather than just pattern matching.
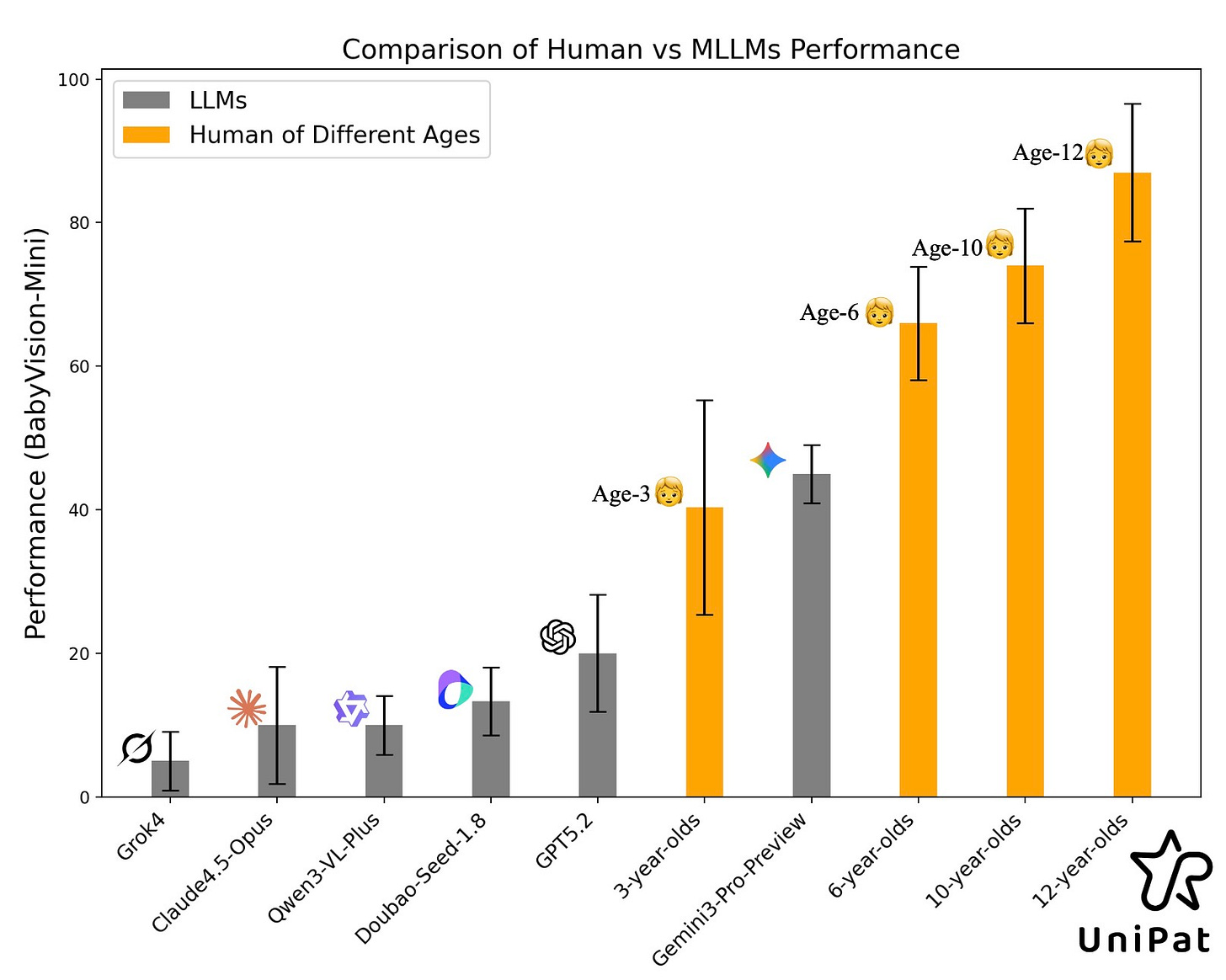
Why it matters: This highlights a critical “illusion of competence” in current models. They can describe complex scenes but fail at simple visual logic.
Paper | Leaderboard
ReinPool & FastLane
Two papers this week tackle the scalability of advanced retrieval. ReinPool reduces the storage cost of multi-vector embeddings (like ColBERT) by 1000x using reinforcement learning to pool tokens. FastLane speeds up the retrieval process itself, addressing the computational bottleneck of late-interaction models.
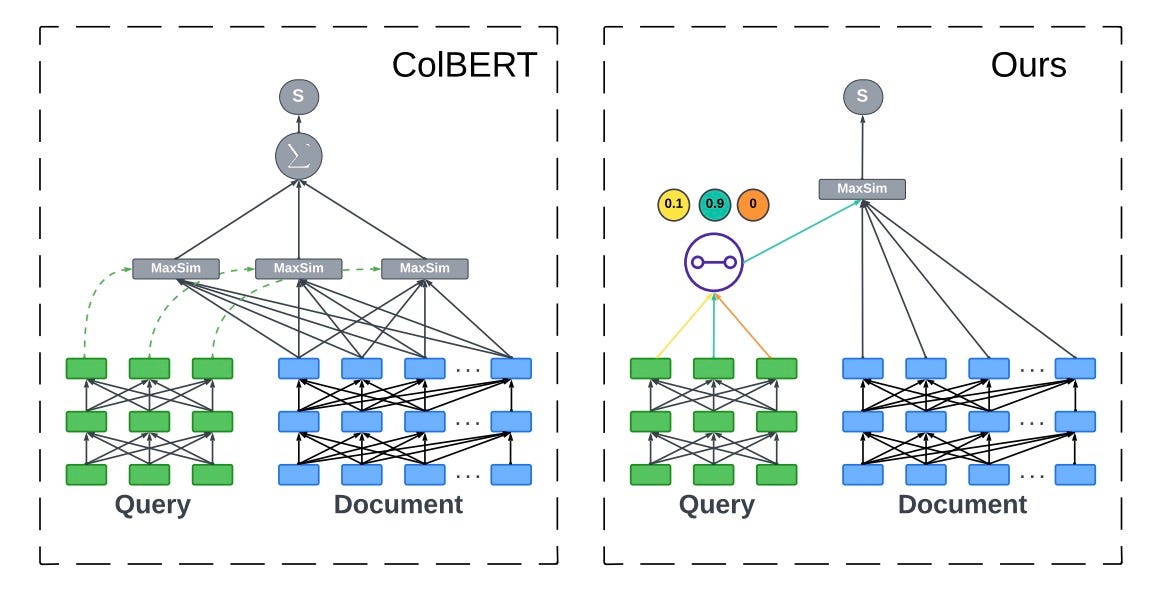
Why it matters: We all want the accuracy of ColBERT-style retrieval, but the cost is often prohibitive. These innovations make high-precision, fine-grained multimodal search feasible at scale, allowing us to index massive video and document libraries without breaking the bank.
ReinPool Paper | FastLane Paper
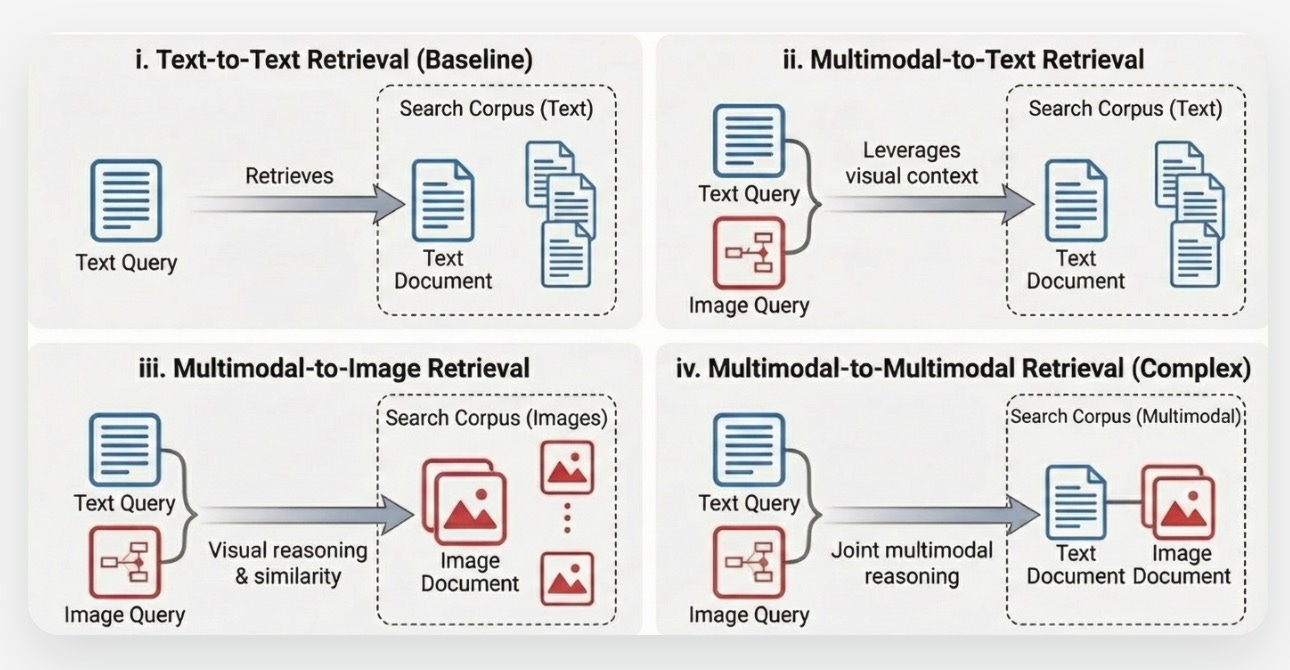
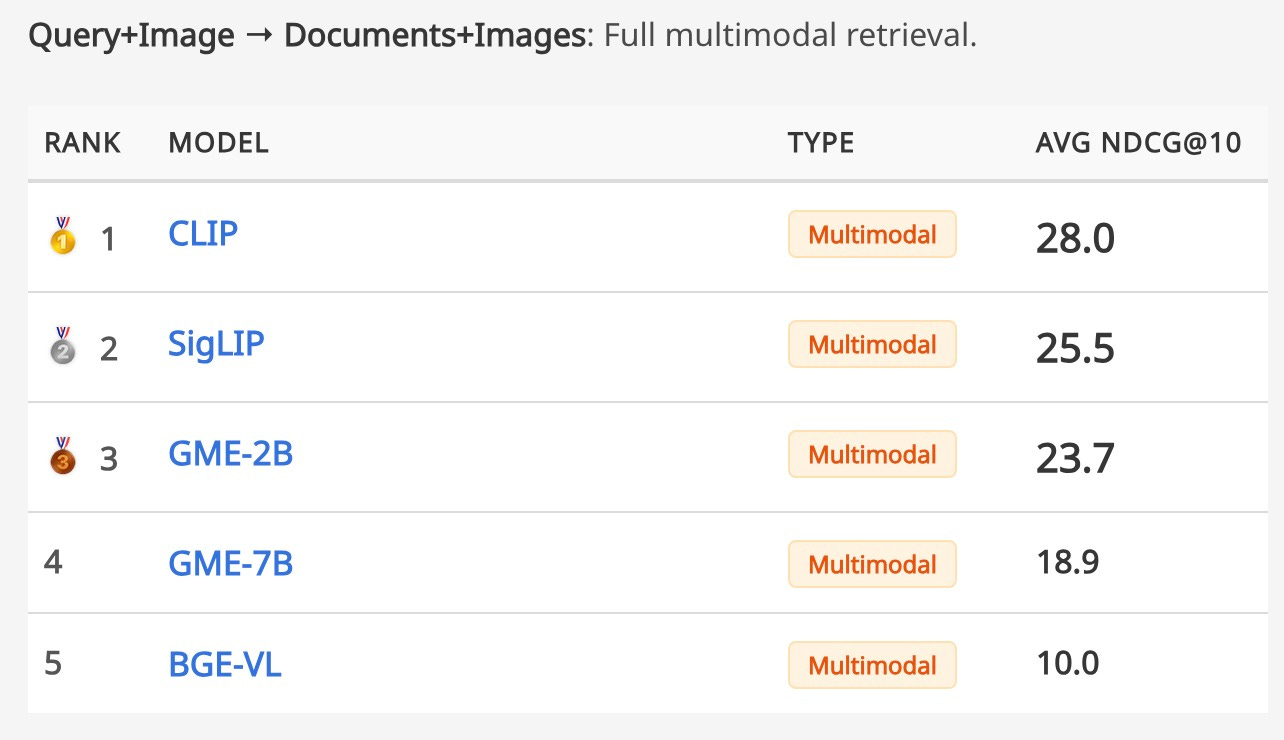
MM-BRIGHT
A new benchmark designed to test “reasoning-intensive” retrieval. It consists of real-world queries from Stack Exchange that require understanding both text and images (like diagrams or code screenshots) to answer correctly.
Learning Latent Action World Models In The Wild
Meta AI researchers have developed a way to learn world models from random internet videos without needing explicit action labels. This allows the model to understand cause-and-effect relationships in diverse, real-world environments.
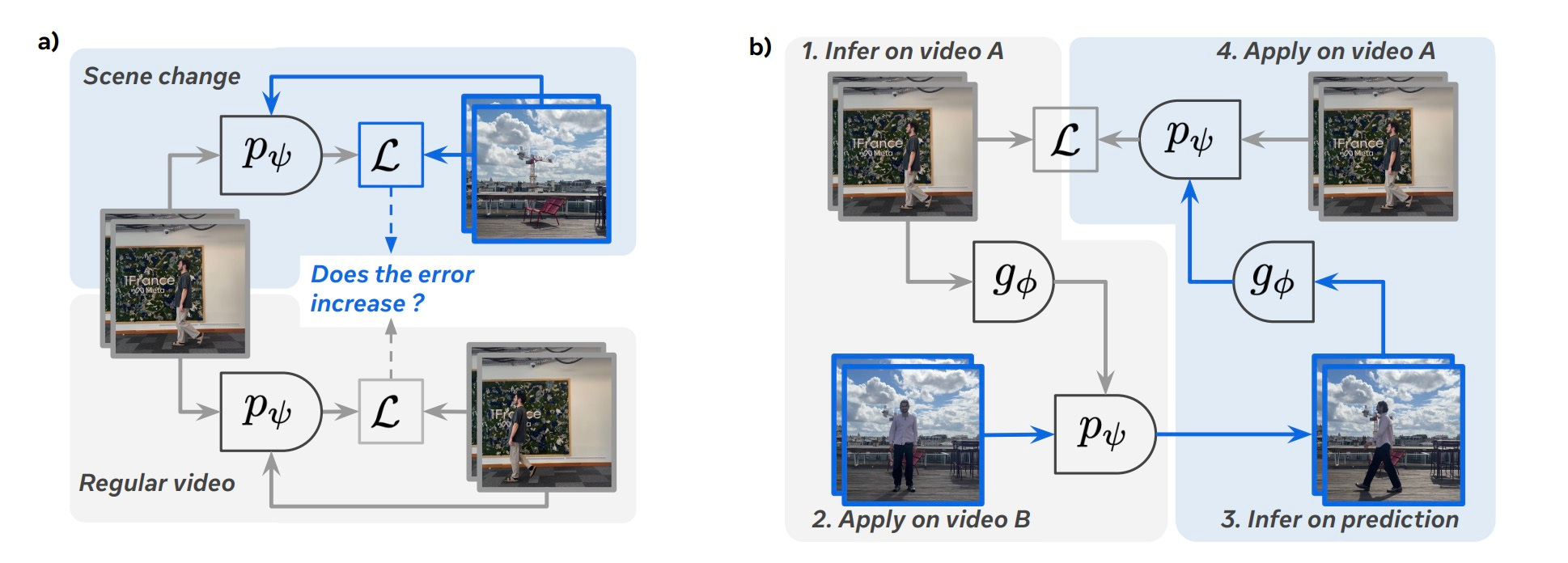
Why it matters: Training robots usually requires expensive, labeled data from simulations. If we can learn physics and dynamics from YouTube videos, we unlock a virtually infinite training set for embodied AI, accelerating the development of general-purpose robots.
Paper
Multilingual-to-Multimodal (M2M) Alignment
This paper proposes a lightweight method to extend multimodal models to new languages without needing huge multimodal datasets. By learning a simple mapping from English, it enables zero-shot cross-modal retrieval in 11 unseen languages.
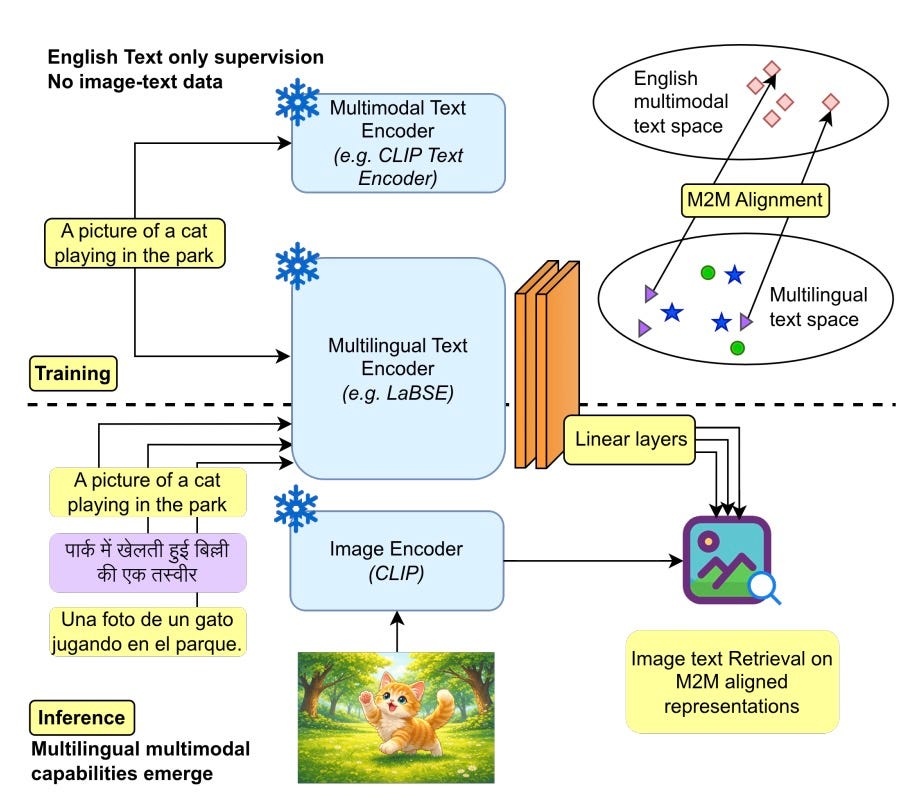
Why it matters: Building multimodal models for every language is inefficient. This approach allows us to leverage the massive investment in English multimodal models and “port” that capability to other languages cheaply, democratizing access to advanced search tools.
Paper
More Research:
- MANZANO: Apple’s simple and scalable unified multimodal model. Paper

ShowUI-π: Flow-based generative models for GUI actions. Paper
- RigMo: Generates rig structure and motion from mesh sequences. Project Page
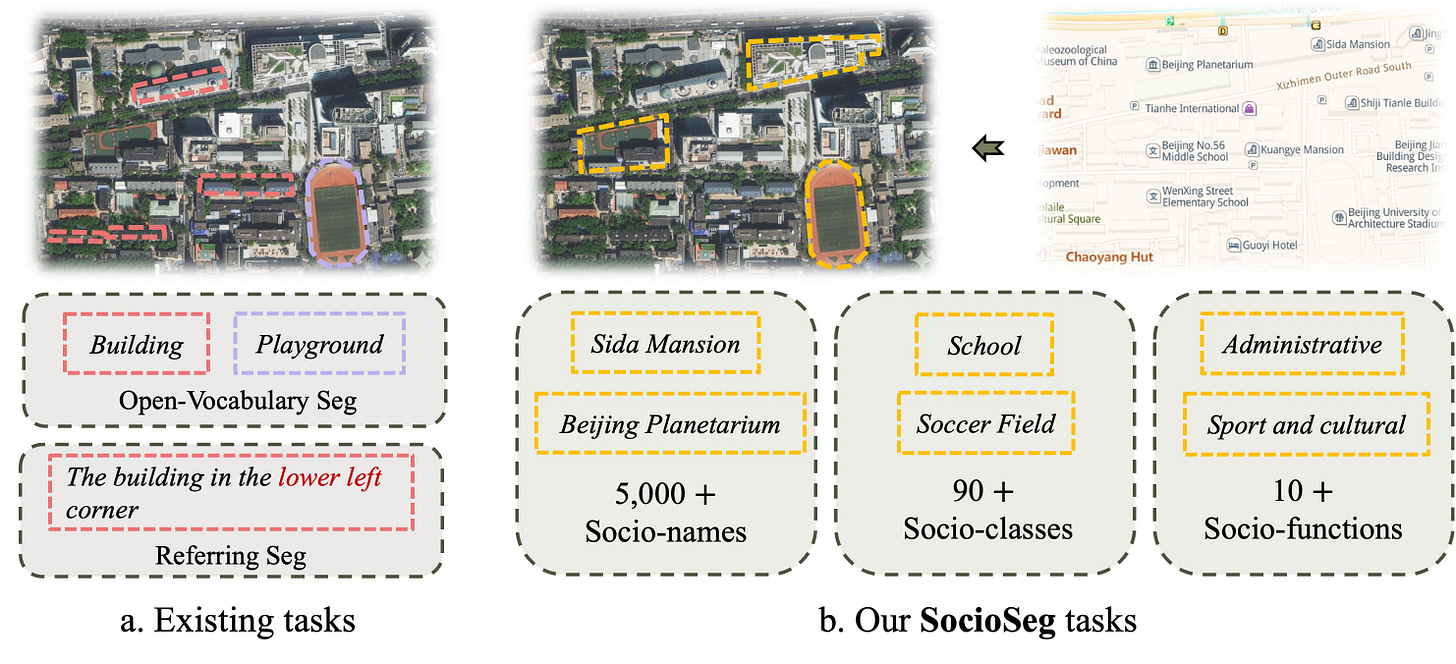
- Urban Socio-Semantic Segmentation: Using VLMs to analyze satellite imagery for social insights. Paper
- CoF-T2I: Using video models as visual reasoners to improve text-to-image generation. Paper
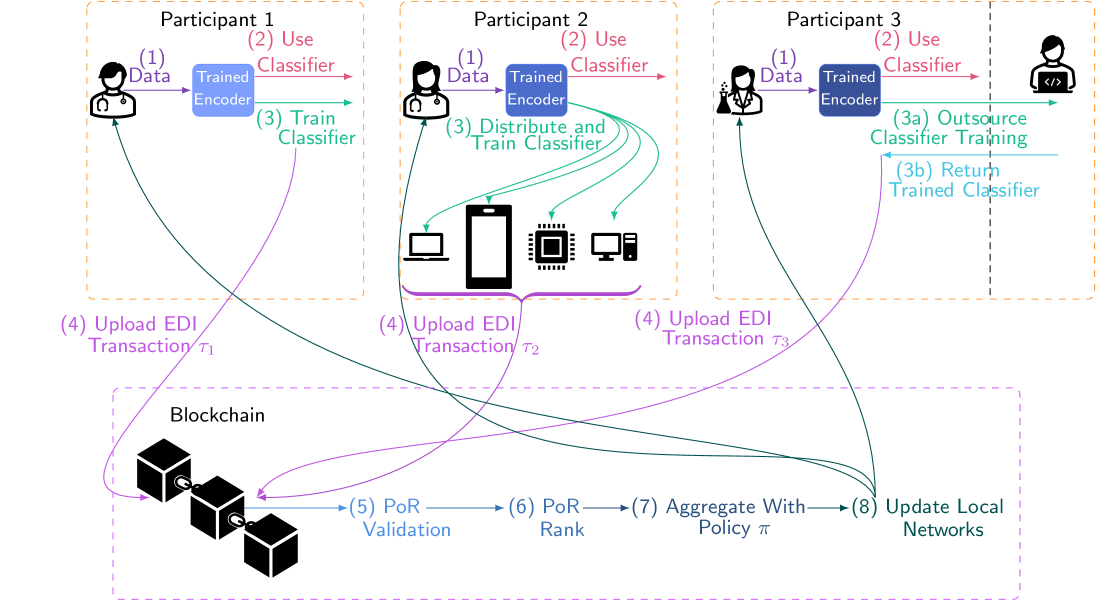
- Proof of Reasoning: Enhancing privacy in federated blockchain learning. Paper
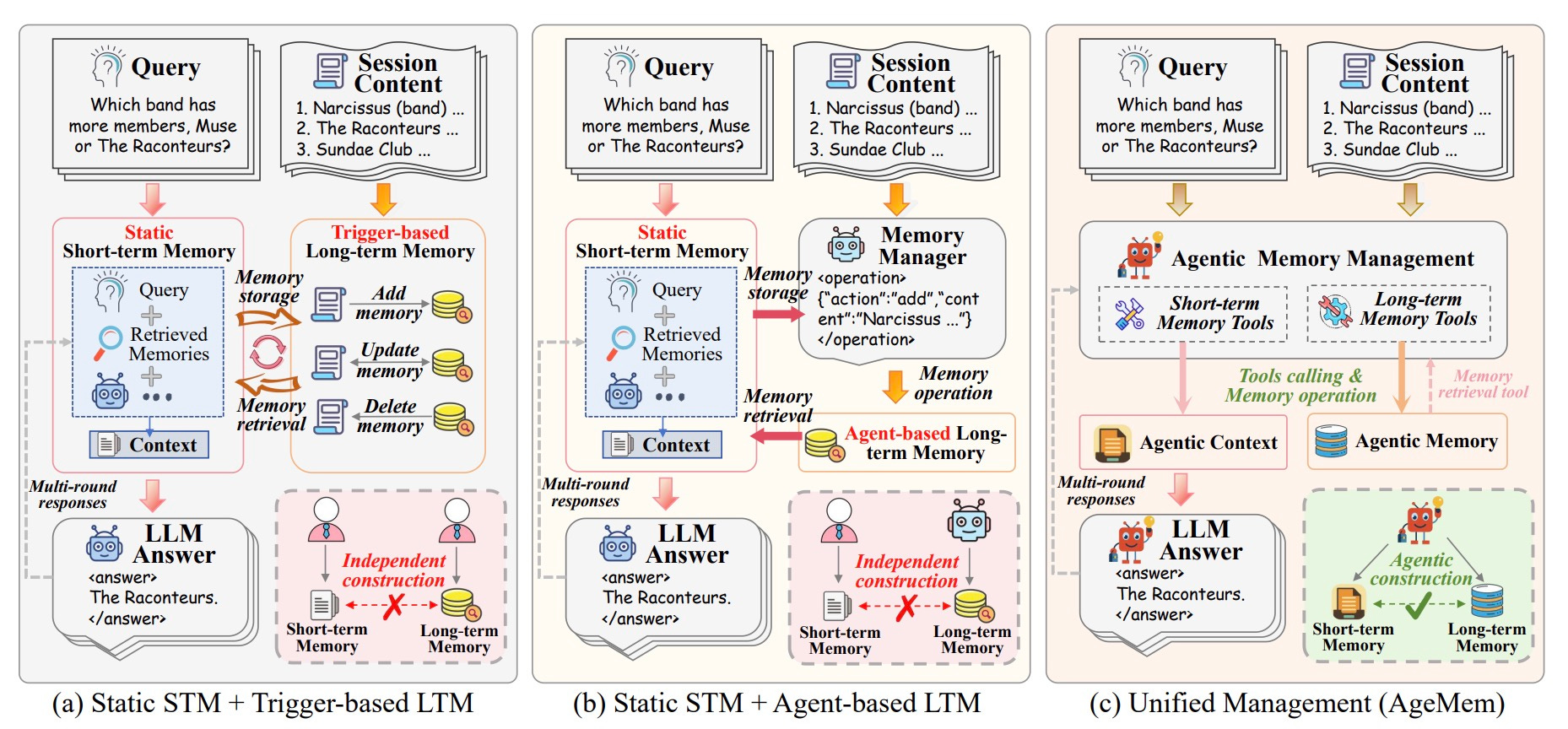
- AgeMem: A unified framework for long-term and short-term agent memory. Paper
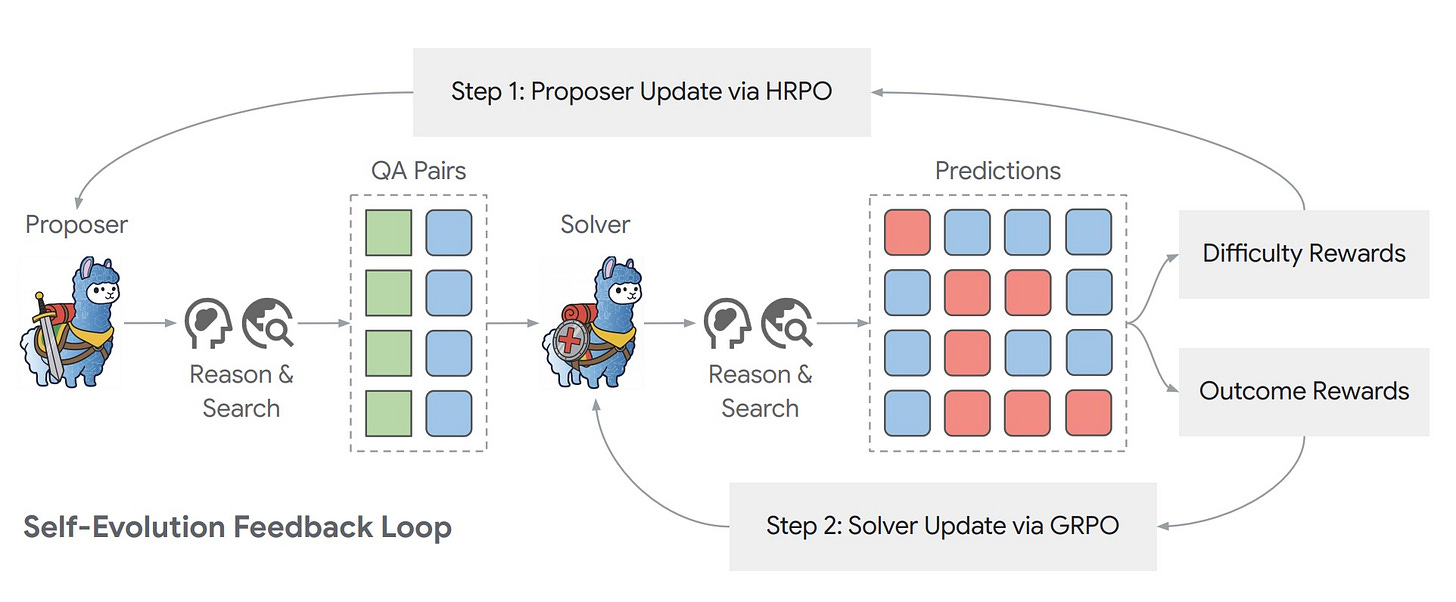
Dr. Zero: Self-evolving search agents that improve without training data. Paper
- Active Context Compression: Agents that autonomously manage their memory like slime mold. Paper
- SimpleMem: Semantic lossless compression for efficient agent memory. Paper
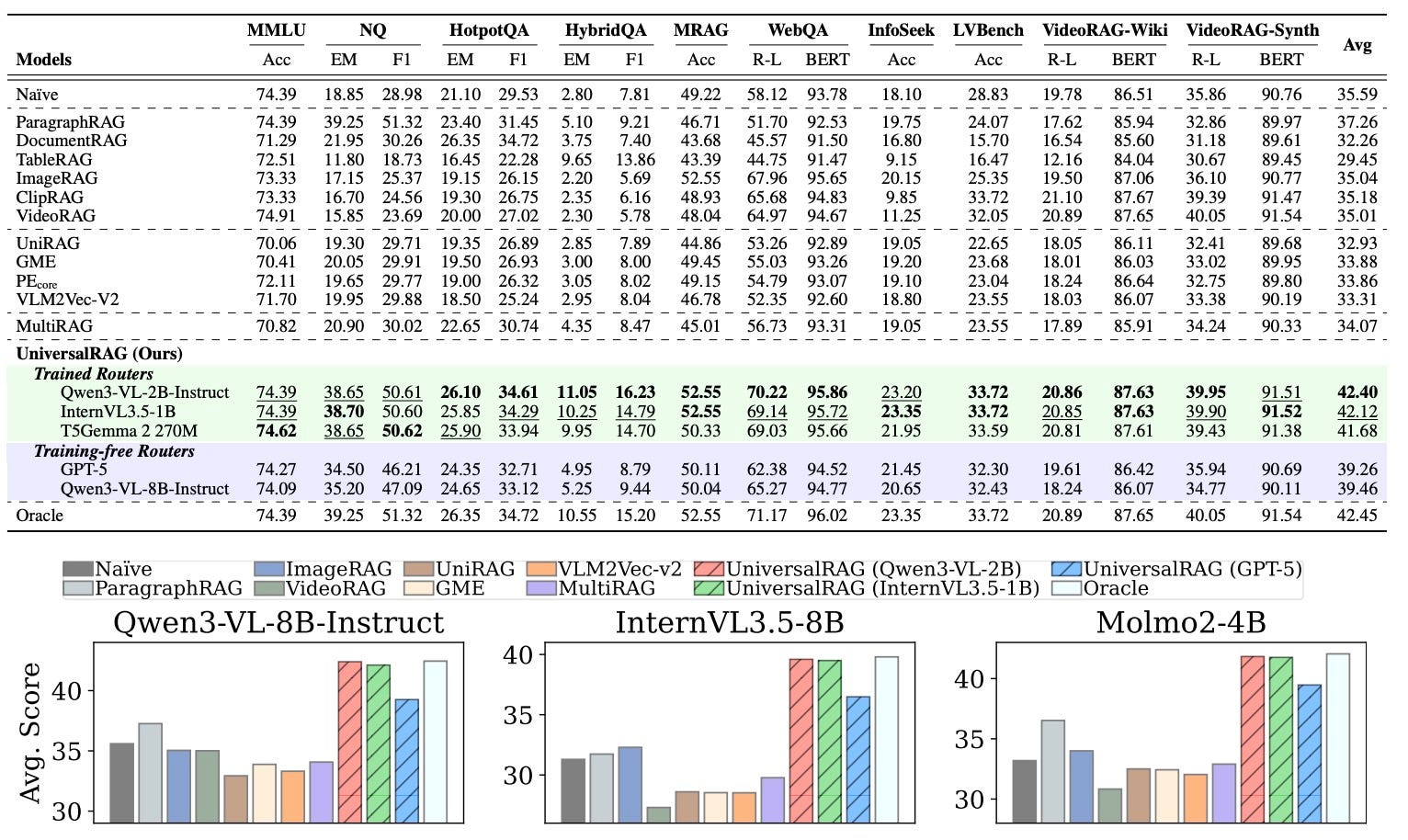
- UniversalRAG: RAG over diverse modalities and granularities. Paper
📈 Trends & Predictions
The “Illusion of Competence” in AI Vision
We often mistake a model’s ability to describe an image for its ability to understand it. The BabyVision benchmark served as a harsh reality check this week, revealing that even our best multimodal models struggle with visual reasoning tasks that a 6-year-old finds trivial. They can write a poem about a sunset but can’t tell you if the sun is to the left or right of the tree.
Why it matters:
- Trust but Verify: We need to stop treating VLM outputs as ground truth. For critical applications (like medical imaging or autonomous driving), “hallucination” isn’t just a quirk; it’s a safety hazard.
- The Reasoning Gap: This highlights that “scaling up” isn’t a magic fix. We need new training paradigms that prioritize reasoning and causality over simple pattern matching.
Human-in-the-Loop: For the foreseeable future, complex visual tasks will require human oversight. The “fully autonomous” visual agent is still further away than the hype suggests, and we need to design our systems with that limitation in mind.
🧩 Community + Shoutouts
•Better Long Videos: Tyler Agg shared a guide on making better long-form videos using models like Nano Banana Pro and Veo3. Guide
•ComfyUI Preprocessors: The ComfyUI Team released new, simplified workflow templates for preprocessors. Announcement
•Kling Motion Control: Workman Lab dropped a quick and informative tutorial on Kling Motion Control. Video
That’s a wrap for Multimodal Monday #41! With ReinPool slashing storage costs by 1000x to make fine-grained retrieval affordable, to BabyVision revealing that our best models score worse than 6-year-olds on basic visual reasoning, to ShowUI-Aloha and ShowUI-π learning to navigate software through visual understanding instead of APIs, Compact models like Ministral 3 and STEP3-VL-10B achieve frontier performance on consumer hardware and more.
